ترکیبات فعال قارچ های دارویی با فعالیت ضد ویروسی
عفونت های ویروسی سلامت انسان را تحت تأثیر قرار داده. و باعث همه گیری های گسترده و مرگ و میر در سراسر جهان شده است. ویروسها همچنین می توانند مشکلات اقتصادی بزرگی را برای جامعه در سطح جهانی ایجاد کنند.
ترکیبات فعال زیستی جدا شده از قارچ ها (اعم از خوراکی و غیرقابل خوردن) فعالیت بالقوه ای را در برابر ویروس ها نشان داده اند.

در این بررسی ، ما ترکیبات طبیعی قارچی را که توانایی مهار برخی از ویروس های بیماری زای انسان را دارند. مانند موارد زیر :
- ویروس نقص ایمنی انسانی
- ویروس دنگی
- ویروس هرپس سیمپلکس
- ویروس تبخال گاو
- ویروس آنفولانزا
- ویروس سندرم تنفسی
- ویروس هپاتیت
ما بر روی مسیرهای بیوسنتتیک ترکیبات فعال زیستی قارچی تمرکز کردیم. و دانش فعلی را در مورد مکانیسم های ضد ویروسی عملکرد آنها و اهداف خاص مورد بررسی قرار دادیم.
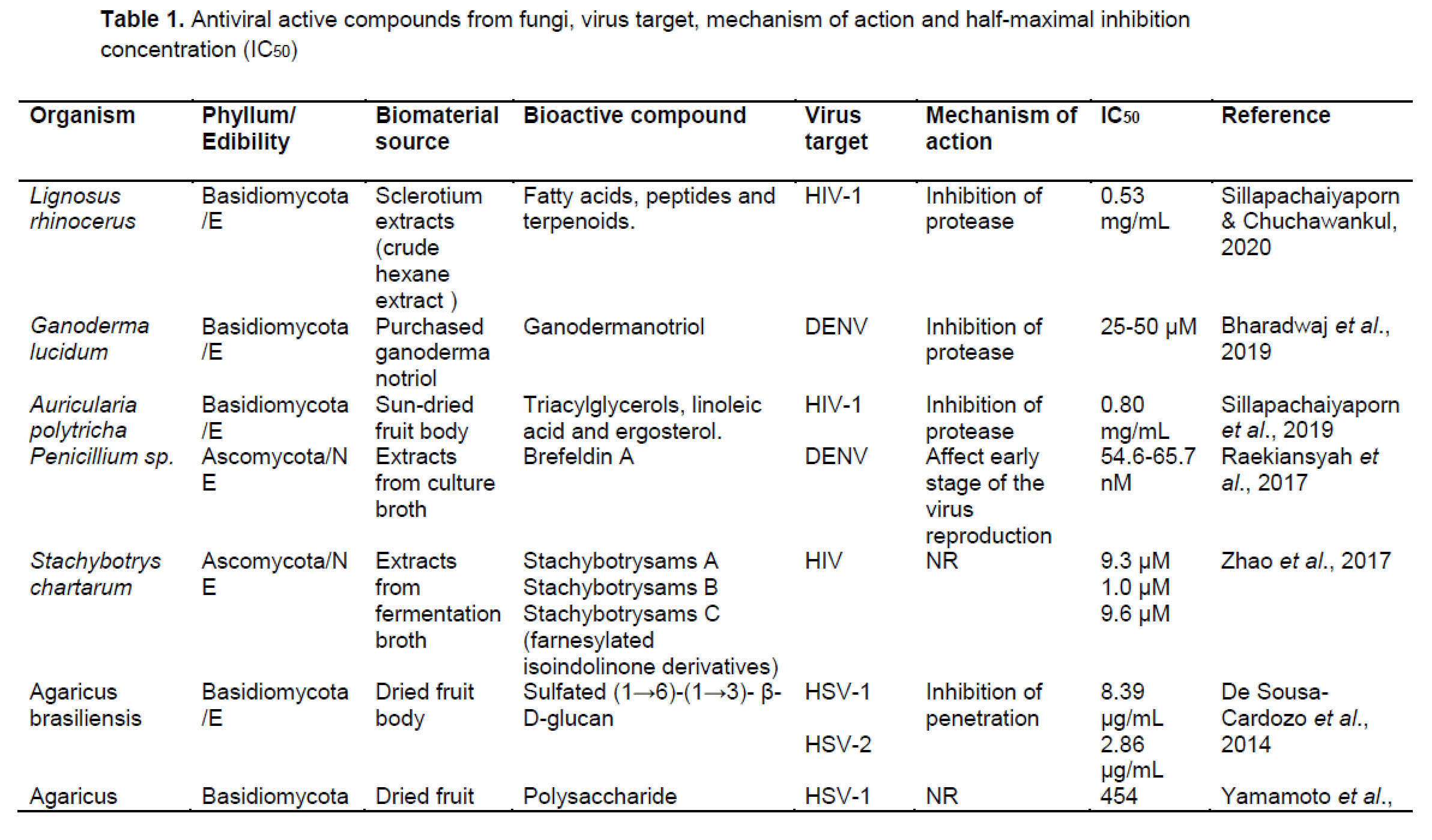
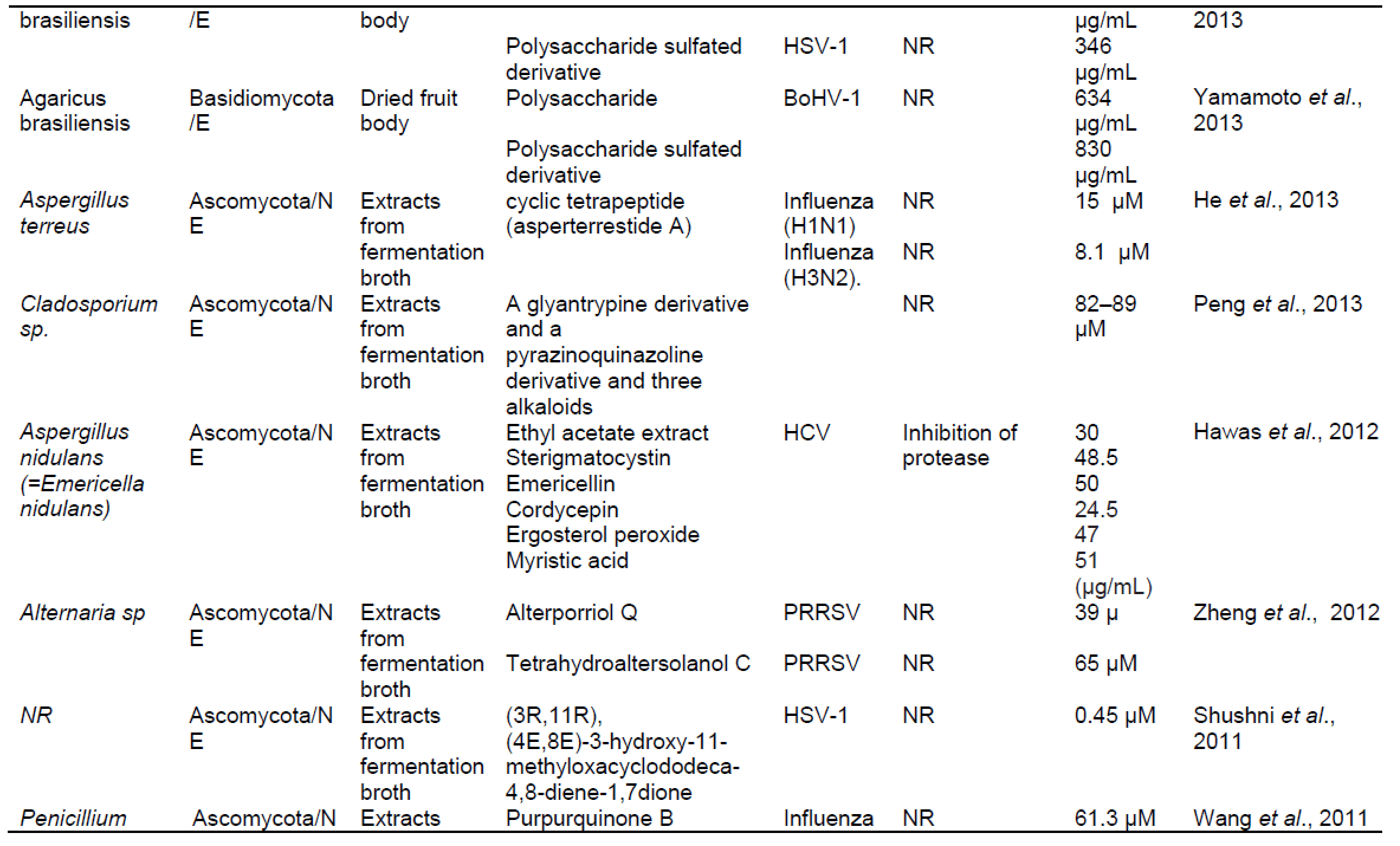
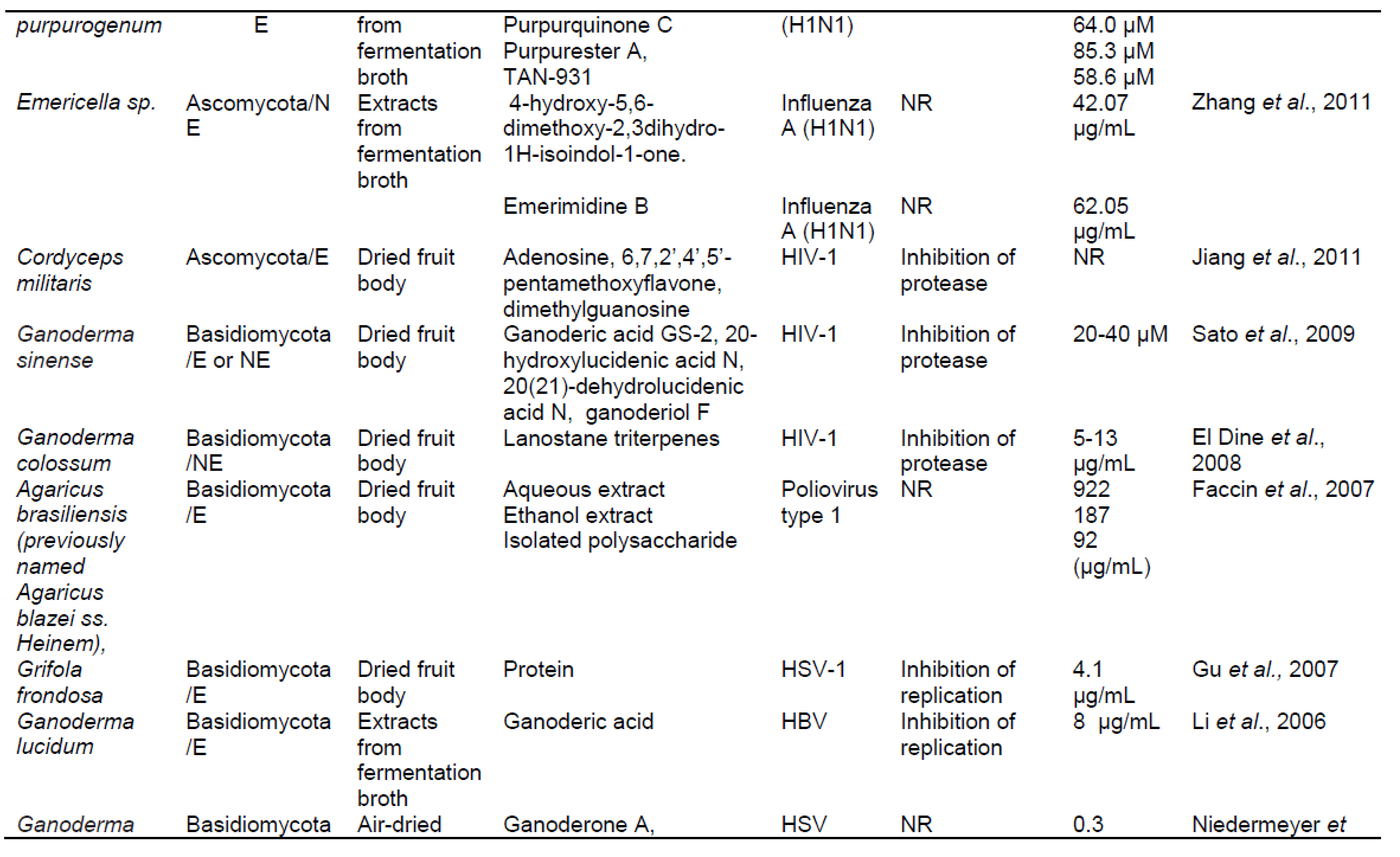
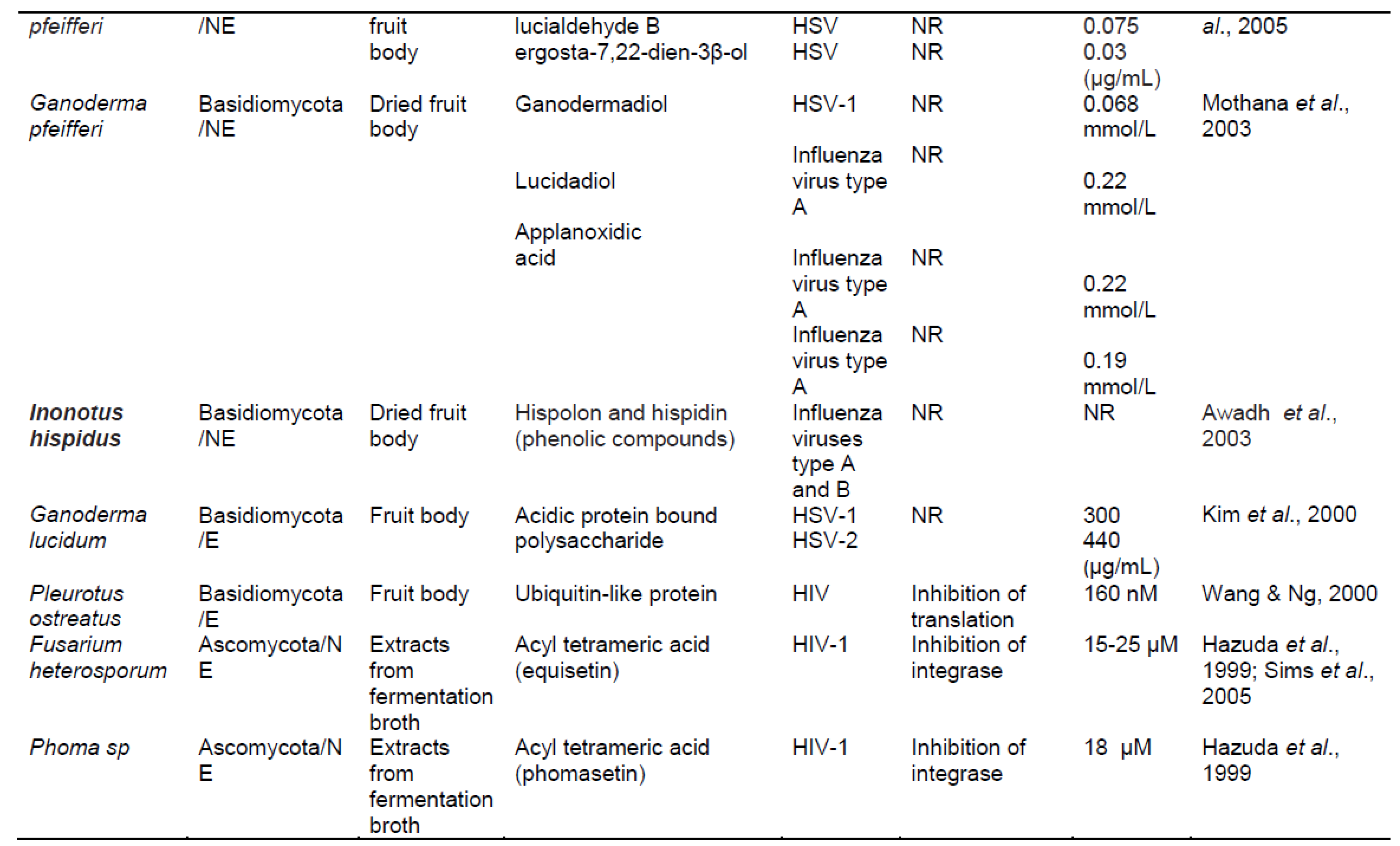
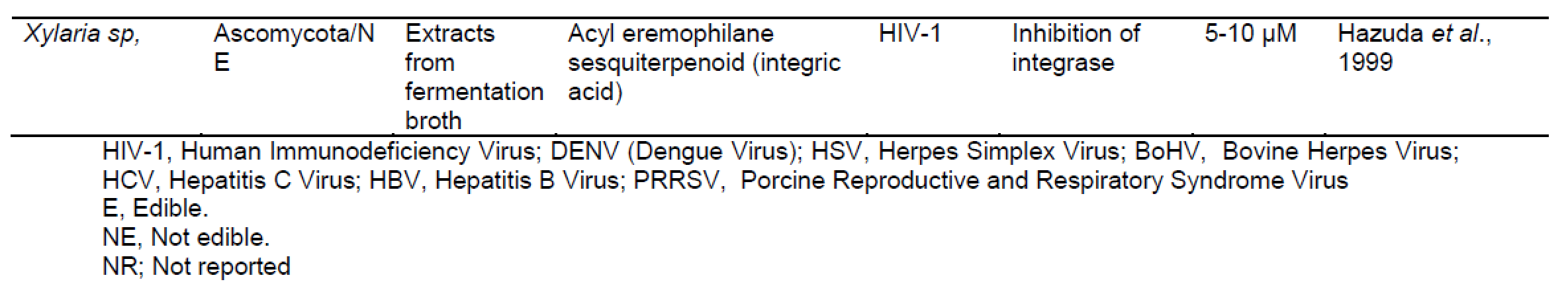
ترکیبات فعال زیستی قارچی قادر به مهار تولید مثل ویروس ، جلوگیری از نفوذ ویروس. تکثیر یا ترجمه و همچنین اثر اینتگراز یا پروتئاز هستند. ترکیبات قارچی قادر به مهار پروتئاز مانند گانودرماتریول ، ارگوسترول ، ترپنوئیدها ، گانودریک اسید GS-2 ، گانودریول ، استریگماتوسیستین ، آمریسلین ، کوردیسپین ، پراکسید ارگوسترول ، اسید میریستیک. و سایر موارد ، در حال حاضر برای جامعه اهمیت زیادی دارد ، زیرا ممکن است پتانسیل درمان عفونت های شدید تنفسی ویروسی را داشته باشد. .
[/fusion_text]
قارچ ها منبع طبیعی بالقوه مولکول های فعال زیستی هستند. که می توانند برای درمان عفونت های ویروسی. که یکی از عوامل اصلی بیماری در سراسر جهان است ، مورد استفاده قرار گیرند. با این حال ، تحقیقات گسترده ای در مورد آزمایشات بالینی برای معرفی داروهای ضد ویروسی جدید به بازار مورد نیاز است. ترکیبات قارچ های دارویی
Bioactive compounds from fungi with antiviral activities: Mechanism of action and biosynthetic pathways
Abstract and Figures
Fungi