سوالات و پاسخ های آن زیر از وبسایت بیمارستان فیلادلفیا استخراج و ترجمه شده است. وبسایت دکتر مهدیزاده هیچ نظری در ارتباط با صحیح یا غلط بودن آن ندارد:
At what age can someone be infected with HPV?
Anyone can be infected with HPV regardless of their age. For example, if a pregnant woman has HPV, her baby can be born with an HPV infection.
در چه سنی می تواند فردی به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده شود؟
هرکسی بدون توجه به سن خود می تواند به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده شود. به عنوان مثال ، اگر یک زن باردار به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) مبتلا باشد ، کودک وی می تواند با عفونت زگیل تناسلی (HPV) متولد شود.
If someone is infected with one type of HPV and their immune system clears it, are they immune to other types of HPV too?
Immunity to one type of HPV does not afford protection against the other types. The current vaccine protects against 9 different types of HPV, which protects against those most likely to cause disease
اگر کسی به یک نوع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده باشد و سیستم ایمنی بدن آن را پاک کند ، آیا در برابر انواع دیگر HPV نیز مقاوم است؟
مصونیت در برابر یک نوع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) در برابر انواع دیگر محافظت نمی کند. واکسن موجود در برابر 9 نوع مختلف زگیل تناسلی (HPV) محافظت می کند ، که از افرادی که به احتمال زیاد باعث بیماری می شوند محافظت می کند.
If a person is diagnosed with cervical HPV, does that mean they also have HPV anally if they’ve had anal intercourse, and is there a test for the presence of HPV anally?
A person found to have HPV in cells of the cervix may or may not have the infection in cells of the anus. The virus does not travel in the body; however, people often do not know when they were infected. So, it is possible that the cells of the anus could have been infected if the HPV exposure that resulted in cervical infection occurred during relations that also involved anal intercourse. Unfortunately, there is not an HPV-related test for cells of the anus.
اگر فردی مبتلا به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) دهانه رحم تشخیص داده شود ، به این معنی است که اگر مقاربت مقعدی داشته باشد نیز HPV آنال دارد و آیا آزمایشی برای وجود زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آنالی وجود دارد؟
ممکن است فردی مبتلا به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) در سلولهای دهانه رحم باشد و ممکن است در سلول های مقعد عفونت نداشته باشد. ویروس در بدن حرکت نمی کند. با این حال ، مردم اغلب نمی دانند چه زمانی آلوده شده اند. بنابراین ، ممکن است سلولهای مقعد آلوده شده باشند ، در صورت قرار گرفتن در معرض زگیل تناسلی (HPV) که منجر به عفونت دهانه رحم می شود ، در طی روابطی که شامل رابطه مقعدی نیز باشد ، رخ داده است. متأسفانه ، آزمایش مربوط به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) برای سلولهای مقعد وجود ندارد.
If a person is diagnosed with genital HPV, does that mean they also have HPV orally, and is there a test for the presence of HPV orally?
The HPV virus does not travel to other parts of the body, so a genital infection does not automatically mean an oral infection. Unfortunately, no test is available to check for HPV orally at this time.
اگر فردی با زگیل تناسلی (HPV) تشخیص داده شود ، به این معنی است که زگیل تناسلی (HPV) دهانی هم دارد و آیا آزمایشی برای وجود زگیل تناسلی (HPV) دهانی وجود دارد؟
ویروس زگیل تناسلی (HPV) به سایر نقاط بدن مهاجرت نمی کند ، بنابراین عفونت دستگاه تناسلی به طور خودکار به معنای عفونت دهانی نیست. متأسفانه ، در حال حاضر هیچ آزمایشی برای بررسی زگیل تناسلی (HPV) به صورت دهانی در دسترس نیست.
How long does an HPV infection last?
HPV infections can last up to 24 months before the immune system eliminates the infection. During this time, most people do not know they are infected. This is why it is difficult to stop transmission of the virus.
عفونت زگیل تناسلی (HPV) چه مدت طول می کشد؟
قبل از اینکه سیستم ایمنی بدن عفونت را از بین ببرد ، عفونت های زگیل تناسلی (HPV) می توانند تا 24 ماه ادامه داشته باشند. در این مدت ، بیشتر مردم نمی دانند که آلوده هستند. به همین دلیل جلوگیری از انتقال ویروس دشوار است.
[/fusion_text]
What does it mean when people say an HPV infection “cleared”? Is the infection gone or is it dormant? Can it still be spread to someone else?
HPV virus can cause persistent infections. This means that when a person is infected, the virus is reproducing in the cells that line the infected area. It does not live silently inside of cells like herpes viruses. This means that when the immune system “clears” the infection, it is no longer present, and therefore it cannot be spread to someone else.
However, what is important to understand is that many people have HPV infections without symptoms; so they do not realize they are infected. Further, since a Pap test checks for cellular changes and not the presence of virus, a “negative” Pap test does not mean that no HPV infection is present. It only means that the cells that line the cervix do not currently show signs of damage caused by a persistent HPV infection. This is why it is important to get regular Pap tests.
وقتی مردم می گویند عفونت زگیل تناسلی (HPV) “پاک” شده یعنی چه؟ آیا عفونت از بین رفته است یا خاموش است؟ آیا هنوز هم می توان آن را به شخص دیگری انتقال داد؟
ویروس زگیل تناسلی (HPV) می تواند باعث عفونت های مداوم شود. این بدان معنی است که وقتی فردی آلوده می شود ، ویروس در سلول هایی که منطقه آلوده را پوشانده اند ، تولید مثل می شود. مانند ویروس های تبخال در سلول بی صدا زندگی نمی کند. این بدان معنی است که وقتی سیستم ایمنی بدن عفونت را “پاک” می کند ، دیگر وجود ندارد و بنابراین نمی تواند به شخص دیگری منتقل شود.
با این حال ، آنچه مهم است که درک شود این است که بسیاری از افراد عفونت زگیل تناسلی (HPV) بدون علائم دارند. بنابراین آنها نمی فهمند که آلوده شده اند. بعلاوه ، از آنجا که آزمایش پاپ آزمایش تغییرات سلولی و عدم وجود ویروس را بررسی می کند ، آزمایش پاپ تست “منفی” به معنای عدم وجود عفونت زگیل تناسلی (HPV) نیست. این فقط به این معنی است که سلول های دهانه رحم در حال حاضر علائم آسیب ناشی از عفونت مداوم زگیل تناسلی (HPV) را نشان نمی دهند. به همین دلیل انجام آزمایشات پاپ طبیعی به طور منظم از اهمیت برخوردار است.
How does HPV cause cancer?
HPV infects epithelial cells that line mucosal surfaces of the body. When HPV enters these cells, such in the throat, genital tract or anus, it causes the cells to produce HPV proteins. In most cases, the immune system recognizes the cells that are infected and eliminates them, clearing the infection. However, in some instances a persistent infection occurs causing the cells to mutate, or change. These mutations can ultimately lead to cancer.
زگیل تناسلی (HPV) چگونه باعث سرطان می شود؟
زگیل تناسلی (HPV) سلولهای اپیتلیال را که سطوح مخاطی بدن را پوشانده اند آلوده می کند. وقتی زگیل تناسلی (HPV) وارد این سلول ها مانند گلو ، دستگاه تناسلی یا مقعد می شود ، باعث تولید پروتئین های زگیل تناسلی (HPV) توسط سلول ها می شود. در بیشتر موارد ، سیستم ایمنی بدن سلولهای آلوده را تشخیص داده و با از بین بردن عفونت ، آنها را از بین می برد. با این حال ، در برخی موارد بسیار کم ، عفونت مداوم ایجاد می شود و باعث جهش یا تغییر سلول ها می شود. این جهش ها در نهایت می توانند منجر به سرطان شوند.
Am I really at risk of getting HPV?
HPV is spread through genital contact, most often, but not always, during sex. It can also spread through oral sex. Most people don’t know they have HPV, so they often don’t realize they are spreading the virus. Since HPV is so common, if you are intimate with anyone, the best way to reduce your chance of getting infected is to be vaccinated with the HPV vaccine.
آیا واقعاً در معرض خطر ابتلا به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) هستم؟
زگیل تناسلی (HPV) از طریق تماس دستگاه تناسلی ، اغلب ، نه همیشه ، در حین رابطه جنسی منتشر می شود. همچنین می تواند از طریق رابطه جنسی دهانی گسترش یابد. اکثر مردم نمی دانند که زگیل تناسلی (HPV) دارند ، بنابراین اغلب متوجه نمی شوند که ویروس را گسترش می دهند. از آنجا که زگیل تناسلی (HPV) بسیار رایج است ، اگر با کسی صمیمی باشید ، بهترین راه برای کاهش احتمال ابتلا ، واکسیناسیون با واکسن زگیل تناسلی (HPV) است.
How common is HPV?
HPV is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases among both men and women in the United States. Currently, about 79 million Americans are infected with HPV and every year, about 14 million new infections occur.
زگیل تناسلی (HPV) چقدر شایع است؟
زگیل تناسلی (HPV) یکی از شایعترین بیماریهای مقاربتی در مردان و زنان در ایالات متحده است. در حال حاضر ، حدود 79 میلیون آمریکایی به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده شده اند و هر ساله ، حدود 14 میلیون عفونت جدید رخ می دهد.
How do I know if my partner or I have been exposed to HPV?
Because most people do not develop symptoms of infection, they do not know they are infected. To avoid or decrease the chance of exposure, you can abstain from sexual activity, limit the number of sexual partners you have and use condoms. Unfortunately, other than abstinence, none of these methods offers complete protection.
چگونه می توان فهمید که همسر من یا من در معرض زگیل تناسلی (HPV) قرار گرفته ایم؟
از آنجا که بیشتر افراد علائم عفونت پیدا نمی کنند ، نمی دانند که آلوده هستند. برای جلوگیری یا کاهش احتمال مواجهه ، می توانید از فعالیت جنسی خودداری کنید ، تعداد شرکای جنسی خود را محدود کرده و از کاندوم استفاده کنید. متأسفانه ، به غیر از پرهیز ، هیچ یک از این روش ها محافظت کامل ندارند.
Is HPV deadly?
آیا زگیل تناسلی (HPV) کشنده است؟
خیر، در بعضی از افراد ویروس باعث تغییراتی در سلول ها می شود اما با تقویت سیستم ایمنی بدن میتوان آنها را برطرف نمود.
Once a person has HPV, can he or she get rid of it?
Yes, in fact, most people (9 of every 10) do clear the infection within two years, often never having symptoms. Those who don’t clear the infection (the remaining 1 of every 10 people) may suffer from genital warts, cervical cancer or other cancers.
هنگامی که فردی به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) مبتلا شد ، می تواند از شر آن خلاص شود؟
بله ، در واقع ، اکثر افراد (از هر 10 نفر 9 نفر) ظرف مدت دو سال عفونت را پاک می کنند ، و اغلب هرگز علائمی ندارند. کسانی که عفونت را پاک نکنند (از هر 10 نفر 1 نفر باقیمانده) ممکن است از زگیل تناسلی (HPV) رنج ببرند.
Can someone be infected with more than one type of HPV?
Yes, you can be infected with more than one type of HPV at a time.
آیا کسی می تواند به بیش از یک نوع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده شود؟
بله ، می توانید همزمان به بیش از یک نوع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده شوید.
Do I need to worry about HPV if my boyfriend and I always use a condom?
If your boyfriend has an HPV infection (with or without symptoms), you can still be infected with HPV even when using a condom for two reasons. First, because condoms aren’t foolproof at containing the virus, you could still be infected and, second, while HPV is most often transmitted during sexual intercourse, it can also be transmitted during oral sex or during genital-to-genital contact.
آیا اگر من و دوست پسرم همیشه از کاندوم استفاده کنیم آیا باید نگران زگیل تناسلی (HPV) باشم؟
اگر دوست پسر شما به عفونت زگیل تناسلی (HPV) مبتلا باشد (با علائم یا بدون آن) ، به دو دلیل هنوز هم می توانید با HPV آلوده شوید. اول ، به دلیل اینکه کاندوم ها به طور کامل محافظت نمیکنند، شما هنوز هم ممکن است آلوده شوید و دوم اینکه ، با وجود اینکه زگیل تناسلی (HPV) اغلب در هنگام مقاربت جنسی منتقل می شود ، همچنین می تواند در حین رابطه دهانی یا تماس پوست ناحیه تناسلی به به پوست ناحیه تناسلی منتقل شود.
How long does it take for symptoms of HPV to appear?
People can be infected with HPV for years, or even decades, before they experience any symptoms of infection. This is why women should get regular Pap screenings. Because Pap screenings show early signs of changes in cells of the cervix (precancerous changes), treatment is often more successful than after physical symptoms, such as bleeding and pain, appear.
چه مدت طول می کشد تا علائم زگیل تناسلی (HPV) ظاهر شود؟
افراد می توانند سالها یا حتی دهه ها قبل از اینکه علائم عفونت را تجربه کنند ، به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده شوند. به همین دلیل زنان باید به طور منظم آزمایش غربالگری پاپ را انجام دهند. از آنجا که غربالگری پاپ ، علائم اولیه تغییرات سلولهای دهانه رحم را نشان می دهد ، درمان اولیه اغلب موفقیت آمیزتر از زمانی است که علائم جسمی مانند خونریزی و درد شروع شده است.
If someone has genital warts, does that mean HPV virus is still present?
If a person has outward signs of infection, such as genital warts, he or she can transmit the virus. However, it is important to realize that people can also transmit HPV when they do not have any symptoms. Additionally, even if someone has genital warts removed, they may still be infected and able to transmit the virus.
اگر کسی زگیل تناسلی دارد ، آیا این بدان معناست که ویروس زگیل تناسلی (HPV)هنوز وجود دارد؟
اگر فردی دارای علائم بیرونی مانند زگیل های تناسلی باشد ، می تواند ویروس را منتقل کند. با این حال ، مهم است که درک کنیم افراد همچنین می توانند زگیل تناسلی (HPV) را انتقال دهند در صورتی که هیچ علائمی نداشته باشند. علاوه بر این ، حتی اگر کسی زگیل تناسلی (HPV) را برداشته باشد ، ممکن است همچنان آلوده شده و قادر به انتقال ویروس باشد.
Even though I got the HPV vaccine, I got genital warts. Will I always have them?
Even if you had the HPV vaccine, you could still develop genital warts if you were infected with a strain of HPV not contained in the vaccine. You may want to consider visiting your healthcare provider to confirm the diagnosis of genital warts. If you do have genital warts, your doctor can go over treatment options with you depending on your particular situation. You can read the information about treating genital warts from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Regarding whether you will always have genital warts, it is difficult to say. In most people, their immune system will eventually clear the infection and the warts will go away, but for some, they may remain. We have no way of telling whether an individual’s immune system is likely to clear the infection or not.
حتی اگر واکسن زگیل تناسلی (HPV) گرفتم ، به زگیل های تناسلی مبتلا شدم. آیا همیشه آنها را خواهم داشت؟
حتی اگر واکسن زگیل تناسلی (HPV) زده باشید ، اگر به استرین ای از زگیل تناسلی (HPV) که در واکسن وجود ندارد آلوده شوید، ممکن است دچار زگیل های تناسلی شوید. اگر زگیل های دستگاه تناسلی دارید ، پزشک بسته به شرایط خاص شما می تواند گزینه های درمانی را با شما بررسی کند. می توانید اطلاعات مربوط به درمان زگیل تناسلی را از مراکز کنترل و پیشگیری بیماری ها بخوانید.
در مورد اینکه آیا شما همیشه زگیل تناسلی خواهید داشت ، گفتن مشکل است. در بیشتر افراد ، سیستم ایمنی بدن آنها در نهایت عفونت را از بین می برد و زگیل ها از بین می روند ، اما برای برخی ، ممکن است باقی بمانند. ما هیچ راهی برای تشخیص اینکه آیا سیستم ایمنی بدن فرد می تواند عفونت را برطرف کند یا خیر ، نداریم.
How soon will genital warts appear if I get infected with HPV? Am I really at risk of getting HPV?
Genital warts typically develop four weeks to eight months after contracting one of the types of HPV that cause genital warts. However, HPV can also replicate without causing symptoms for several years before genital warts appear.
در صورت ابتلا به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) ، چه زمانی زگیل های تناسلی ظاهر می شوند؟ آیا واقعاً در معرض ابتلا به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) هستم؟
زگیل های تناسلی معمولاً چهار هفته تا هشت ماه پس از ابتلا به یکی از انواع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) که باعث زگیل های تناسلی می شوند ، ایجاد می شوند. با این حال ، زگیل تناسلی (HPV) می تواند چندین سال قبل از ظهور زگیل های تناسلی بدون ایجاد علائم ، تکثیر کند.
How soon after an HPV infection does cervical cancer develop?
Progression from an initial HPV infection to cancer requires prolonged infection with one of the types of HPV that causes cancer. For this reason, cervical cancer typically develops 20 to 25 years after the initial HPV infection. Regular Pap tests and HPV tests will help your doctor monitor for precancerous changes to the cells of the cervix.
چه مدت پس از عفونت زگیل تناسلی (HPV) سرطان دهانه رحم ایجاد می شود؟
پیشرفت از عفونت اولیه زگیل تناسلی (HPV) به سرطان نیاز به عفونت طولانی مدت با یکی از انواع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) است که باعث سرطان می شود. به همین دلیل ، سرطان دهانه رحم معمولاً 20 تا 25 سال پس از عفونت اولیه زگیل تناسلی (HPV) ایجاد می شود. آزمایشات منظم پاپ و آزمایش زگیل تناسلی (HPV) به پزشک کمک می کند تا تغییرات پیش سرطانی در سلول های دهانه رحم را کنترل کند.
Transmission-related questions
سوالات مربوط به انتقال
I recently had an LEEP procedure to remove high-risk cells from my cervix following a positive Pap test. Can I still pass HPV on to my partner after having this procedure done?
The loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) does not rid you of HPV. It rids you of some cells that are showing signs of changes resulting from long-term infection. If you are with the same partner that you were with prior to your diagnosis, it is possible the partner was already exposed to the type of HPV you are infected with. If you are with a new partner and that person was not previously exposed to the type of HPV that you have (either naturally or through vaccination), you might expose your partner.
من اخیراً یک روش LEEP برای حذف سلولهای پر خطر از دهانه رحم خود به دنبال آزمایش پاپ مثبت انجام داده ام. آیا بعد از انجام این روش آیا هنوز هم می توانم زگیل تناسلی (HPV) را به شریک زندگی خود منتقل کنم؟
روش لیپ (LEEP) شما را از شر HPV خلاص نمی کند. بلکه از برخی سلول ها که نشانه هایی از تغییرات ناشی از عفونت طولانی مدت دارند ، از بین می برد. اگر با همان شریکی که قبل از تشخیص خود بوده اید هستید ، ممکن است شریک زندگی قبلاً در معرض نوع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) شما قرار گرفته باشد. اگر با یک شریک جدید هستید و آن شخص قبلاً در معرض نوع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) شما نبوده است (چه به صورت طبیعی و چه از طریق واکسیناسیون) ، ممکن است او را آلوده کنید.
Can a person spread HPV to someone after getting the HPV vaccine?
The HPV vaccine protects against nine types of HPV. Two earlier versions protected against two or four types. The types of HPV in the vaccine protect against the most common causes of cancer and genital warts. If, after being vaccinated, a person is infected with a type of HPV that was included in the vaccine, he or she is unlikely to be infected and, therefore, wouldn’t spread the virus. However, if a vaccinated person is exposed to an HPV type not in the vaccine, they could potentially be infected and spread the virus to others.
آیا شخصی می تواند پس از تزریق واکسن زگیل تناسلی (HPV) ، ویروس زگیل تناسلی (HPV) را به شخصی منتقل کند؟
واکسن کنونی زگیل تناسلی (HPV) در برابر نه نوع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) محافظت می کند. دو واکسن قبلی در برابر دو یا چهار نوع محافظت می شوند. انواع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) موجود در واکسن در برابر شایع ترین دلایل سرطان و زگیل های تناسلی محافظت می کند. اگر پس از واکسیناسیون ، شخصی به نوعی زگیل تناسلی (HPV) که در واکسن وجود داشت آلوده شود ، بعید است که آلوده شود و بنابراین ویروس را گسترش نمی دهد. با این حال ، اگر یک فرد واکسینه شده در معرض نوع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) که در واکسن وجود ندارد قرار بگیرد ، احتمالاً ممکن است آلوده شده و ویروس را به دیگران انتقال دهد.
Is it possible for a person who says they are a virgin to spread HPV?
It is possible to spread the virus through intimate contact that does not include intercourse, such as genital-to-genital contact or oral-to-genital contact. So, it is possible that someone who has not had intercourse could be infected with HPV and spread it to others.
آیا فردی که می گوید باکره است می تواند ویروس زگیل تناسلی (HPV) را گسترش دهد؟
گسترش ویروس از طریق تماس پوست بدون دخول جنسی، مانند تماس بین پوست ناحیه تناسلی نیز انجام می شود. بنابراین ممکن است کسی که مقاربت نکرده است به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده شده و آن را به دیگران منتقل کند.
If I am infected with HPV orally, can I pass the virus to my children if I kiss them?
While the studies looking at HPV transmission orally are minimal, it is generally agreed upon by the scientific community that HPV is spread orally through more intimate forms of engagement, such as oral sex or “open-mouth” (French) kissing; so kissing your daughter would not be likely to spread the virus to her if you were infected with HPV orally.
اگر از طریق دهان به ویروس زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده شده باشم ، آیا می توانم ویروس را به کودکان خود منتقل کنم اگر آنها را ببوسم؟
در حالی که مطالعات انجام شده درباره انتقال زگیل تناسلی (HPV) به صورت دهانی کم است ، اما به طور کلی مورد توافق جامعه علمی است که زگیل تناسلی (HPV) از طریق اشکال صمیمی تری از نامزدی ، مانند رابطه جنسی دهانی یا بوسیدن “دهان باز” (فرانسوی) به صورت خوراکی منتشر می شود. بنابراین اگر از طریق دهان به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده شوید ، بوسیدن دخترتان احتمالاً ویروس را به او منتقل نخواهد کرد.
I have heard HPV can be transmitted by skin-to-skin contact. So, if a woman has HPV, can I or my children get it by being around her?
No. HPV is not transmitted by simply being near or touching someone who has it. The reference to skin-to-skin contact refers to intimate interactions, such as genital-to-genital or oral-to-genital contact.
من شنیده ام که زگیل تناسلی (HPV) می تواند از طریق تماس پوست به پوست منتقل شود. بنابراین ، اگر زنی به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) مبتلا شده است ، آیا من یا فرزندانم می توانم با بودن در کنار او به آن مبتلا شویم؟
نه. زگیل تناسلی (HPV) به سادگی در نزدیکی یا لمس کسی که به آن مبتلا باشد منتقل نمی شود. اشاره به تماس پوست با پوست به تماس های خیلی صمیمی مانند تماس دستگاه تناسلی با دستگاه تناسلی یا دهان به دستگاه تناسلی و حتی دهان با دهان اشاره دارد.
I have never been diagnosed with HPV or genital warts, so how could my child have recurrent respiratory papillomatosis?
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, or RRP, is chronic infection of the vocal cords and lungs caused by passage through a birth canal infected with HPV. RRP is primarily caused by two types of HPV that also commonly cause genital warts, types 6 and 11. Because many people are infected with HPV and never have symptoms, they do not know they have an HPV infection. Therefore, unfortunately, it is possible that you could have had an undiagnosed HPV infection during pregnancy that led to your child’s infection.
من هرگز مبتلا به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) یا زگیل تناسلی نشده ام ، بنابراین چگونه ممکن است فرزندم پاپیلوماتوز تنفسی داشته باشد؟
پاپیلوماتوز تنفسی یا RRP ، عفونت مزمن تارهای صوتی و ریه ها است که گاهی به دلیل عبور نوزاد از مجاری زایمان آلوده به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) ایجاد می شود. RRP در درجه اول توسط دو نوع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) ایجاد می شود که معمولاً باعث ایجاد زگیل تناسلی می شوند ، نوع 6 و 11. از آنجا که بسیاری از افراد به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده هستند و هرگز علائمی ندارند ، آنها نمی دانند که به عفونت زگیل تناسلی (HPV) مبتلا هستند. بنابراین ، متأسفانه ، این احتمال وجود دارد که شما در دوران بارداری به یک عفونت زگیل تناسلی (HPV) بدون علایم مبتلا شوید که منجر به عفونت فرزند شما شده است.
I have been in a monogamous relationship for more than 20 years; however, I was recently diagnosed with genital warts. My wife has never had them. How could I have gotten them?
Your question is a common one. Almost everyone who is sexually active will be infected with HPV at some point. For many, they may never know when or how they were infected for a few reasons. First, symptoms can appear years after the initial infection. Second, the disease can be transmitted without having intercourse. Skin-to-skin contact or oral sex can also transmit the virus. Finally, even people who do not know they are infected and those who do not have any symptoms may still transmit the virus.
من بیش از 20 سال در ارتباط جنسی با یک فرد بوده ام. با این حال ، اخیراً مبتلا به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) شدم. همسرم هرگز زگیل نداشته است. زگیل رو از کجا گرفتم؟
سوال شما یک سوال مشترک است. تقریباً همه افرادی که از نظر جنسی فعال هستند ، در برخی موارد به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده می شوند. به دلایل بسیاری ، ممکن است آنها هرگز ندانند که چه زمانی یا چگونه آلوده شده اند. علت اول این است که علائم زگیل ممکن است سالها پس از آلودگی ظاهر شوند. دوم اینکه این بیماری می تواند حتی بدون رابطه جنسی نیز منتقل شود. تماس پوست با پوست یا رابطه دهانی نیز می تواند ویروس را منتقل کند. بنابراین، حتی افرادی که نمی دانند آلوده هستند و کسانی که هیچ علائمی ندارند ، ممکن است ویروس را منتقل کنند.
Can you get HPV from someone who does not have any symptoms of HPV?
Yes, in fact, most people do not know when they are infected with HPV. So, even if your partner does not have any symptoms of an HPV infection, he or she can still pass the virus to you.
آیا می توانید زگیل تناسلی (HPV) را از شخصی دریافت کنید که هیچ علامتی از HPV نداشته باشد؟
بله ، در واقع ، اکثر مردم نمی دانند چه زمانی به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده شده اند. بنابراین ، حتی اگر شریک زندگی شما هیچ علامتی از زگیل نداشته باشد ، باز هم می تواند ویروس را به شما منتقل کند.
I have heard that you do not need to have intercourse to get HPV. Is that true?
Yes. Although most infections occur following intercourse, HPV may also be passed on during oral sex and genital-to-genital contact. Even more rarely, a mom can transmit the virus to her baby during birth.
من شنیده ام که برای گرفتن زگیل تناسلی (HPV) نیازی به رابطه جنسی نیست. آیا این درست است؟
آره. اگرچه بیشتر عفونت ها پس از مقاربت رخ می دهد ، زگیل تناسلی (HPV) ممکن است در هنگام رابطه جنسی دهانی و تماس پوست ناحیه تناسلی آلوده نیز منتقل شود. حتی به ندرت ، مادر می تواند ویروس را در هنگام تولد به نوزاد منتقل کند.
Can someone get HPV during masturbation?
HPV is transmitted through intimate interactions between an infected person and an uninfected person. They do not have to have intercourse. Genital-to-genital contact can spread the virus. Because masturbation involves touching one’s self, it will not cause someone to become infected with HPV.
آیا کسی می تواند در حین استمنا HP به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) مبتلا شود؟
از آنجا که خودارضایی شامل لمس خود فرد است ، باعث نمی شود کسی به آلوده شود. اچ پی وی از طریق ارتباط نزدیک بین یک فرد آلوده و یک فرد دیکر منتقل می شود. تماس دستگاه تناسلی با دستگاه تناسلی می تواند ویروس را گسترش دهد.
Can a woman pass HPV to a male partner through intercourse?
Yes, a woman can pass the infection to a partner as well as to her baby during birth, although the latter is fairly uncommon. While the infection is most commonly transmitted through intercourse, the virus can also be passed to one’s partner during genital-to-genital contact or oral sex.
آیا زن می تواند زگیل تناسلی (HPV) را از طریق مقاربت به یک شریک مرد منتقل کند؟
بله ، یک زن می تواند عفونت را به یک شریک زندگی و همچنین به نوزاد خود در هنگام تولد منتقل کند ، اگرچه دومی نسبتاً غیر معمول است. ویروس همچنین می تواند در هنگام تماس بین دستگاه تناسلی یا رابطه دهانی به شریک زندگی فرد منتقل شود.
Does having HPV put my unborn baby at risk?
In rare instances, mothers with genital HPV can pass the virus to their baby during vaginal delivery. A small number of these babies go on to develop recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP), a condition in which tumors grow in the throat or lungs, sometimes causing hoarseness and difficulty breathing, talking and swallowing. While the tumors can be surgically removed, they tend to grow back. Some people with RRP require regular surgical intervention. RRP can also cause a disease of the lungs that resembles cystic fibrosis.
A link between HPV and miscarriage, premature delivery or other complications has not been found.
آیا داشتن زگیل تناسلی (HPV) نوزاد متولد نشده من را در معرض خطر قرار می دهد؟
در موارد نادر ، مادران مبتلا به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) دستگاه تناسلی می توانند ویروس را در حین زایمان واژینال به کودک خود منتقل کنند. ارتباطی بین زگیل تناسلی (HPV) و سقط جنین ، زایمان زودرس یا سایر عوارض یافت نشده است.
Can I get the HPV vaccine if I am pregnant?
Although the HPV vaccine has not been found to cause harm to a woman or her fetus, it is recommended to wait until after delivery to start or continue with the series.
If you got the vaccine while you were pregnant, you do not need to take any special precautions.
در صورت بارداری می توان واکسن زگیل تناسلی (HPV) را دریافت کرد؟
اگرچه مشخص نشده است که واکسن زگیل تناسلی (HPV) باعث آسیب رساندن به زن یا جنین او می شود ، اما توصیه می شود تا شروع یا ادامه این سری تا بعد از زایمان صبر کنید.
اگر در دوران بارداری واکسن دریافت کرده اید ، نیازی به اقدامات احتیاطی خاصی ندارید.
I started getting the HPV vaccine and now I am pregnant. Can I still get the other doses of vaccine?
You should wait until after you deliver to get the remaining doses of vaccine. There is no indication that the vaccine causes harm to you or your unborn baby, but it is recommended to wait just to be safe. After you deliver, you can resume the process of getting the remaining doses.
من واکسن زگیل تناسلی (HPV) را شروع کردم و اکنون باردار هستم. آیا هنوز هم می توان دوزهای دیگر واکسن را دریافت کرد؟
برای دریافت دوزهای باقیمانده واکسن باید منتظر بمانید تا بعد از زایمان. هیچ نشانه ای وجود ندارد که این واکسن به شما یا نوزاد متولد شده شما آسیب برساند ، اما توصیه می شود فقط چهت احتیاط صبر کنید. پس از زایمان، می توانید مراحل دریافت دوزهای باقیمانده را از سر بگیرید.
What tests can a woman have related to HPV?
Two tests for women are available:
- Pap test — A Pap test is done by scraping some cells from the cervix and examining them microscopically. A normal result means your cells looked as expected; an abnormal result means that the cells appeared to have undergone some changes. This does not mean you have cervical cancer. In some cases the cell changes are minor and will return to normal when tested in the future. In other cases the cell changes are more dramatic and need to be monitored more closely.
- HPV test — The HPV test determines if the human papillomavirus is present in the cervix.
چه آزمایشاتی می تواند یک زن در رابطه با زگیل تناسلی (HPV) انجام دهد؟
دو تست برای زنان در دسترس است:
تست پاپ
– آزمایش پاپ با تراشیدن برخی سلول ها از دهانه رحم و بررسی میکروسکوپی آنها انجام می شود. نتیجه طبیعی به این معنی است که سلولهای شما همانطور که انتظار می رفت به نظر می رسیدند. نتیجه غیرعادی به این معنی است که سلولها تغییراتی داشته اند. این به این معنی نیست که شما سرطان دهانه رحم دارید. در بعضی موارد تغییرات سلول جزئی است و در آینده به حالت طبیعی برمی گردد. در موارد دیگر تغییرات سلول چشمگیرتر است و باید دقیق تر کنترل شود.
آزمایش زگیل تناسلی (HPV)
– آزمایش زگیل تناسلی (HPV) مشخص می کند ویروس پاپیلومای انسانی در دهانه رحم وجود دارد یا خیر.
If there are no screening tests for men, how can they tell if they have HPV and if so, what is the treatment?
Although there is no approved test for men to know their “HPV status,” most HPV infections resolve without causing any problems. The problems caused by HPV in men can include genital warts, anal and penile cancers, or cancers of the oropharynx. There are ways to check for those:
- Genital warts – If you notice abnormalities in the area of your penis, scrotum or anus, such as warts or blisters, see your healthcare provider.
- Anal cancers – Gay, bisexual, and HIV-positive men may consider annual screening. Although it is not a formal recommendation, these men are at higher risk.
- Penile cancers – No screening tests are currently available, but early signs can include color changes or build-up or thickening of the tissue.
- Cancers of the oropharynx – Signs include issues associated with the throat including pain, constant coughing, voice changes or hoarseness, lumps or masses in the necks, and trouble swallowing or breathing.
اگر هیچ آزمایشی برای تشخیص اچ پی وی در مردان وجود ندارد ، چگونه مردان می توانند تشخیص دهند که زگیل تناسلی (HPV) دارند یا خیر و اگر چنین است ، درمان چیست؟
اگرچه هیچ تست تایید شده ای برای آگاهی از “وضعیت HPV” در مردان وجود ندارد ، اما بیشتر عفونت های زگیل تناسلی (HPV) بدون ایجاد مشکلی برطرف می شوند. مشکلات ناشی از زگیل تناسلی (HPV) در مردان می تواند شامل زگیل های تناسلی ، سرطان های مقعد و آلت تناسلی یا سرطان های دهانه حلق باشد. روش هایی برای بررسی این موارد وجود دارد:
زگیل های تناسلی – در صورت مشاهده ناهنجاری در ناحیه آلت تناسلی ، بیضه یا مقعد ، مانند زگیل یا تاول ، به ارائه دهنده خدمات بهداشتی خود مراجعه کنید.
سرطان های مقعدی – مردان همجنسگرا ، دوجنسیتی و HIV مثبت ممکن است غربالگری سالانه ضرورت داشته باشد.
سرطان های آلت تناسلی مرد – در حال حاضر هیچ آزمایش غربالگری در دسترس نیست ، اما علائم اولیه می تواند شامل تغییر رنگ یا تجمع یا ضخیم شدن بافت باشد.
سرطان های حفره حلق – علائم شامل مواردی است که با گلو همراه است از جمله درد ، سرفه مداوم ، تغییر صدا یا گرفتگی صدا ، توده ها یا توده های گردن و مشکل در بلع یا تنفس.
Is there a treatment for HPV?
Most HPV infections, however, clear on their own in a few years without causing any health problems. there are supportive treatments for the health problems caused by HPV, such as genital warts and cancers.
آیا درمانی برای زگیل تناسلی (HPV) وجود دارد؟
بیشتر عفونت های زگیل تناسلی (HPV) در طی چند سال خود به خود برطرف می شوند و هیچ مشکلی برای سلامتی ایجاد نمی کنند. درمان های حمایتی برای مشکلات ناشی از زگیل تناسلی (HPV) مانند زگیل های تناسلی و سرطان ها وجود دارد.
If I am infected with HPV, will getting vaccinated make the infection go away?
No. The vaccine only protects people against types of HPV to which they were not previously exposed. It does not treat an existing infection or protect against that type of HPV.
اگر من به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده باشم ، آیا واکسیناسیون باعث از بین رفتن آن می شود؟
خیر. واکسن فقط از افراد در برابر انواع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) که قبلاً در معرض آنها قرار نگرفته است محافظت می کند. ویروس موجود را درمان نمی کند و در برابر آن نوع زگیل تناسلی (HPV) محافظت نمی کند.
Does a negative Pap test mean that I am not infected with HPV?
No. A Pap test is one in which cells isolated from the cervix are examined under a microscope for precancerous changes caused by a persistent, or long-term, HPV infection. So, a negative Pap test is good news in that it means the cervical cells appear normal, but it does not give any information about a person’s HPV status.
A test that specifically detects HPV is also available. Although this test does measure the presence of HPV virus in the cervical cells, it does not provide information about whether that infection will remain long term or eventually cause cancer. Because many younger women get an HPV infection that is cleared by their immune systems, the HPV test can often be positive, causing unnecessary concern; therefore, it is not recommended for most women younger than 30 years of age.
آیا آزمایش پاپ تست منفی به این معنی است که من به زگیل تناسلی (HPV) آلوده نیستم؟
خیر. تست پاپ آزمایشی است که در آن سلولهای جدا شده از دهانه رحم زیر میکروسکوپ از نظر تغییرات سلولی ناشی از عفونت زگیل تناسلی (HPV) مداوم یا طولانی مدت مورد بررسی قرار می گیرند. بنابراین ، آزمایش پاپ منفی به این معنی است که سلولهای دهانه رحم طبیعی به نظر می رسند ، اما هیچ اطلاعاتی در مورد وجود ویروس زگیل تناسلی (HPV) فرد نمی دهد.
آزمایشی که به طور خاص زگیل تناسلی (HPV) را تشخیص می دهد نیز موجود است. اگرچه این آزمایش وجود ویروس زگیل تناسلی (HPV) در سلولهای دهانه رحم را اندازه گیری می کند ، اما اطلاعاتی در مورد اینکه آیا آن عفونت به مدت طولانی باقی می ماند، ارائه نمی دهد. از آنجا که بسیاری از زنان جوان مبتلا به عفونت زگیل تناسلی (HPV) می شوند و سیستم ایمنی بدن آن برطرف می شود ، این آزمایش ضرورتی نداشته و دادن آن تنها باعث نگرانی بی مورد می شود. بنابراین ، برای اکثر زنان کمتر از 30 سال توصیه نمی شود.
My boyfriend recently had warts on his penis. When I went to the clinic and had a Pap test, the results were normal. Does this mean that I did not get infected, or is there still a chance I could get genital warts?
The types of HPV that cause genital warts typically differ from those that cause cervical cancer. Since a Pap test is meant to identify potential cellular changes that could lead to cervical cancer, it does not provide information about HPV infections with types that cause genital warts. For this reason, your Pap test results do not mean that you did not get infected with HPV when your boyfriend had it. The good news is that for many people, the infection will clear without any symptoms, so you may never experience genital warts like your boyfriend did.
دوست پسر من اخیراً در آلت تناسلی خود زگیل داشته است. وقتی به کلینیک رفتم و آزمایش پاپ دادم ، نتایج طبیعی بود. آیا این بدان معناست که من آلوده نشدم ؟
بله. امکان آلوده شدن هست. پاپ فقط تغیرات سلولی حاصل از آلودگی رو بررسی میکنه و نه وجود یا عدم وجود ویروس رو.
What happens if my Pap test is abnormal?
If you have an abnormal Pap test, an HPV test may be suggested to determine if human papillomavirus DNA is present in the cells of the cervix. If the results of the HPV test are positive, your doctor will determine how frequently you should be tested. In addition to HPV and Pap tests, a colposcopy or biopsy may be suggested. A colposcopy visualizes the cells of the cervix and a biopsy takes a sample of cervical cells.
اگر آزمایش پاپ من غیرطبیعی باشد چه اتفاقی می افتد؟
اگر آزمایش پاپ غیرطبیعی دارید ، آزمایش زگیل تناسلی (HPV) برای تعیین وجود ویروس پاپیلومای انسانی در سلول های دهانه رحم پیشنهاد می شود. اگر نتایج آزمایش زگیل تناسلی (HPV) مثبت باشد ، پزشک تعیین می کند که چند بار باید آزمایش شوید. علاوه بر آزمایش های HPV و Pap ، ممکن است کولپوسکوپی یا بیوپسی نیز پیشنهاد شود. کولپوسکوپی سلول های دهانه رحم را بررسی می کند و نمونه برداری از سلول های دهانه رحم با نمونه برداری انجام می شود. در صورت غیر طبیعی بودن پاپ، تقویت سریع سیسم ایمنی بدن ضرورت دارد.
How frequently should you get a Pap test?
Women are recommended to get their first Pap test at age 21, and then once every three years until they turn 29. Women who are 30 to 65 years old should have both Pap and HPV tests performed every five years, or a Pap test alone every three years. Women who have an irregular Pap test or who are at risk due to other factors, such infection with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) or previous diagnosis of cervical cancer, may be required to get tested more frequently.
Find out more on the CDC’s page, “What should I know about screening?”
Find out if you qualify for free or reduced cost screening through the National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program (NBCCEDP) and where near you offers the program.
Can HPV tests replace Pap tests?
No, HPV tests should not replace routine Pap tests for two reasons:
- The tests are not measuring the same thing. Pap tests detect changes in the cells of the cervix that could lead to cancer, whereas HPV tests detect human papillomavirus DNA in the cells of the cervix. A positive HPV test could be the result of a recent infection or a chronic infection.
- The tests are recommended for slightly different age groups; routine Pap tests are recommended for all women 21 years and older, whereas HPV tests are recommended for women 30 years and older and only those women between 21 and 29 who have had an irregular Pap test.
Is there a test to determine if I have HPV?
Yes. The HPV test is used to determine if HPV DNA is present in the cells of the cervix. Positive results mean that your cervix has the types of HPV commonly linked to cervical cancer; however, a positive result does not mean you have cervical cancer. Based on the results, your doctor will determine how frequently you should be tested and whether other tests should be performed. Currently, HPV tests are recommended for all women 30 years and older and any woman 21 to 29 years old who has had an irregular Pap test.
When a person is tested for STDs is HPV testing included?
Sexually transmitted disease (STD) testing is not the same for every person as it depends upon individual risk factors. For HPV, there is no test for males. For females, HPV can be detected by either Pap tests or an HPV test. The Mayo Clinic has a good discussion regarding how to determine what STD tests you may need and what is available.
I got all necessary doses of the HPV vaccine. Do I still need to get Pap tests?
Yes. The HPV vaccine does not contain all of the types of HPV that can cause cervical cancer; therefore, it is important to continue getting Pap tests.
If I have had an abnormal Pap test in the past, can I still get the HPV vaccine?
Yes. You should still get the HPV vaccine even if you have had an abnormal Pap test because even if you have been infected with HPV, it is not likely that you have been infected with all of the types that the vaccine protects against. So, you can still benefit from protection afforded by the HPV vaccine.
How long after receiving the HPV vaccine does it take for the vaccine to work?
The immune system takes one to two weeks to generate immunity to vaccines or infections. In the case of HPV vaccine, the first dose (and the second one if the person is on the three-dose series), generates a primary immune response, so people will have some immunity, but protection can vary from one person to another. The last dose (given at least six months after the first dose) is important because it enhances the memory immune response. A person will have the greatest protection beginning about one to two weeks after receiving their last dose of the vaccine.
Questions about who should get HPV vaccine
Who should get the HPV vaccine and how many doses?
The HPV vaccine is recommended for adolescents between 9 and 12 years of age, and all teenagers and adults between 13 and 26 years of age who did not get the vaccine when they were younger.
Two doses of the HPV vaccine are recommended for those younger than 15 years of age, with the second dose administered six months after the first one. Those 15 years and older should receive three doses of HPV vaccine with the second dose given one to two months after the first, and the third dose given six to 12 months after the first.
Learn more about why this is the recommended age group by watching the short video below.
If I have received the first dose of HPV vaccine, is it safe to be intimate? Am I protected from HPV?
People who have received one dose of the HPV vaccine may have some protection, but the additional dose or doses (depending upon age) offer additional protection. Further, if you or your partner were already infected with a type of HPV, the vaccine will not prevent transmission of that type.
I think I had the HPV vaccine about six years ago, but I am not certain. Should I get the shot? And if I do, but I was vaccinated before, will anything happen?
You should talk with your healthcare provider to see if they know whether you were vaccinated and if so, what type of HPV vaccine you received and how many doses were given. However, if that is not an option and you are uncertain, you can still get the vaccine. Extra doses are not likely to have negative effects.
I had the HPV vaccine, but have since given birth to a child. Do I need the HPV vaccine again?
No, people who have been vaccinated against HPV do not need to be revaccinated after giving birth.
If someone already has HPV, does it help to get the HPV vaccine?
Yes. Typically, people with HPV have not been infected with all of the strains contained in the vaccine, so the vaccine could protect them from strains to which they have not been exposed previously. However, the vaccine will not help treat or protect against types of HPV to which the person has already been exposed.
I have received two doses of the HPV vaccine, but missed my third dose. Do I need to start again?
For those 15 years of age and younger, the HPV vaccine is now given in two doses. So, depending on your age, you may not need a third dose:
- If you are under 15 years old and your first two doses were at least six months apart, you do not need a third dose.
- If you are 15 years or older, you still need the third dose; it should be separated from the first dose by six to 12 months.
I have heard there is a new HPV vaccine that protects against more types of HPV, but my teens have already had the old one. Do they need to get it again?
The HPV vaccine protects against nine types of HPV (Gardasil 9®). The CDC does not recommend giving this vaccine to people who already had the earlier HPV vaccines (Cervarix® or Gardasil®-4). However, because the vaccine protects against additional types of the virus, individuals may still reasonably get the vaccine. In this case, the person should speak with his/her healthcare provider regarding the relative benefits associated with this choice.
I had two doses of the HPV vaccine a while ago. Now, I hear there is a different one that protects against more types of HPV. Should I get that one and if so, do I need to get all three doses of the new one?
The newer version, Gardasil 9®, is the only version currently available, so you can be protected against more types of the virus by getting the vaccine. The 9-valent vaccine can be used in place of either of the previous two HPV vaccines (Gardasil® and Cervarix®) to complete a vaccination series, so, you do not need to start over again. You would just get the last dose with the current vaccine option. Cervarix is no longer available in the United States.
If you are younger than 15 years old and your first two doses were separated by at least six months, you do not need any additional doses.
I am in my early 20s and would like to get the HPV vaccine, but I don’t know where to get it. What do you suggest?
You should start by checking with your primary healthcare provider. If you cannot get the vaccine from their office, you should also check with your gynecologist, the local health department or a local pharmacy. The manufacturer, Merck, also has an adult vaccine locator on their website that might be of help.
I am concerned that giving the HPV vaccine to young girls will lead them to become sexually active at an earlier age or sexually promiscuous at a later age. Has this been studied?
Yes. A few studies have looked at this and none have found that receiving the HPV vaccine causes girls to become promiscuous or engage in sexual activity at an earlier age. One such study by Robert Bednarczyk and colleagues, published October 2012 in Pediatrics, compared the medical records of 493 girls who received the HPV vaccine and 905 who didn’t. The study found no differences between the two groups in regards to incidence of pregnancies, tests for or diagnosis of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), and contraceptive counseling. Based on these results, the authors of the study reported that the HPV vaccine “was not associated with increased sexual activity-related outcomes.”
I heard that even people who have not received the HPV vaccine have less chance of getting HPV since the vaccine came out. Please explain how this occurred, and why I need to get the HPV vaccine?
The HPV vaccine was introduced in 2006, and according to an article published in the July 2012 issue of Pediatrics, use of the HPV vaccine has resulted not only in lower rates of infection among those who were vaccinated, but also, to some degree, in those who have not been vaccinated. This phenomenon is commonly known as herd immunity.
You should still consider getting the vaccine for two reasons. First, additional studies are needed to reproduce these findings. Second, while herd immunity might lessen your chance of coming into contact with the virus, the vaccine will significantly decrease your chance of infection if you do come into contact with it.
I didn’t get the last dose of the HPV vaccine. Do I need to start over again?
No. You can just resume where you left off.
My daughter is not sexually active. Why should I even consider getting her vaccinated against HPV now?
The HPV vaccine is recommended before the start of sexual activity for two reasons:
- Young people tend to get infected more frequently; in fact, about half of all new infections are diagnosed in girls and young women between 15 and 24 years of age.
- It takes at least six months to complete the series, so even though your daughter may not be active now, or even in six months, it is better to have the series completed sooner rather than later.
I am already sexually active; should I still get the HPV vaccine?
Yes. The reason to get the HPV vaccine even if you are already sexually active is that you will not have been exposed to all of the types of HPV that are contained in the vaccine.
Why does my son need an HPV vaccine since I heard it prevents cervical cancer?
Although HPV is a known cause of cervical cancer, the virus can also cause other cancers of the reproductive tract, anal cancer, penile cancer, genital warts, and on occasion, cancers of the head and neck. In fact, about 1 of every 3 cases of HPV-related cancers are in boys or men. Because vaccinating boys will also decrease the spread of the virus, they will not only protect themselves, but also their sexual partners.
Can my 11-year-old get the HPV vaccine at the same time as other vaccines?
Yes. The HPV vaccine can be given at the same time as other vaccines recommended at this age, including the vaccine for tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (Tdap) and the one for meningococcus. If it is influenza vaccine season, this vaccine can be given as well.
Can I have the vaccine if I’m not a virgin anymore? And will it still be effective?
Yes, you can still get the HPV vaccine even if you have had sexual intercourse. While you may have been exposed to one or more types of HPV, it is unlikely that you would have been exposed to all of the types that the vaccine protects against, so it may still be of benefit for you.
I am 33 years old. Can I get the HPV vaccine?
In October 2018, the vaccine became licensed for people up to 45 years of age, so inquire with your provider.
I finished all doses of the HPV vaccine before I became sexually active, but recently, I had an HPV DNA test that was positive. How can that be, and will the infection go away?
Because the HPV vaccine does not protect against all types of HPV, it is possible that a fully vaccinated person could be infected with a type of HPV that is not contained in the vaccine. Most people will clear any type of HPV infection— but it may take months to do so. In a few people, however, HPV infection will persist and possibly become cancerous. We have no way of knowing who will be affected over the long term. That said, the vaccine protects against the most common types that cause cancer or genital warts.
Questions about HPV vaccine safety
I don’t want to get the HPV vaccine for my child because I have heard that all of the safety studies were completed by the vaccine manufacturer. Is this true?
Vaccine safety is studied by many, many groups not just those who manufacture vaccines. The FDA reviews all data associated with studies completed by vaccine manufacturers as well as visiting manufacturing sites and continuing to monitor the vaccine as long as it is being made. Additionally, the CDC has systems in place to monitor vaccine safety including the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) which allows anyone to report side effects, allowing CDC scientists to watch for trends.
Two additional systems provide a controlled way to test whether the trends are causally associated and to study vaccine safety. The first, the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD), is a collaboration with eight large healthcare organizations from various parts of the United States. Health records are monitored for vaccine receipt and illnesses to study vaccine safety. The second, the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project (CISA), is a national group of vaccine experts from the CDC, seven medical research centers, and other experts who conduct research around specific vaccine safety concerns, provide consultations for individual healthcare providers on specific patients, and review adverse event data. Vaccine manufacturers do not have a role in these studies.
Additionally, the National Academy of Medicine (NAM), previously called the Institute of Medicine (IOM), periodically conducts comprehensive reviews of the literature to monitor vaccine safety. The NAM completed a review related to adverse effects of vaccines, which included HPV, in 2012. Their findings are available online.
More than 200 million doses of HPV vaccine have been given safely throughout the world. More than 100 million of these have been given in the U.S. What we know from all of these data is that the vaccine is safe and it is working to decrease transmission of HPV, genital warts, cervical changes that cause cancer, and juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis.
Can the HPV vaccine cause cancer?
No. Because the HPV vaccine is made using only a single protein from each type of the virus, it can’t cause HPV infection, and, therefore, it can’t cause cervical cancer or other cancers.
My son received the first dose of HPV vaccine and then two months later he was ill with severe stomach pains, rash and a headache. Could this illness have been caused by the vaccine?
It is not likely that your son’s symptoms were the result of his HPV vaccination for a couple of reasons. First, the length of time between the dose and the appearance of symptoms is not what one would expect if the vaccine was the cause. Second, of the three symptoms you mentioned, the only one that was consistently reported in HPV vaccine recipients was headache, and that was typically reported within 15 days of the first dose.
Does the HPV vaccine cause infertility?
No. HPV infections do not cause infertility, except indirectly in cases when they progress to cervical cancer, so it is not biologically plausible that the HPV vaccine would lead to infertility. To the contrary, since the HPV vaccine decreases the number of cases of cervical cancer, it may indirectly decrease the number of women unable to have a baby.
I heard stories of girls developing different illnesses after getting the HPV vaccine. Are these stories true?
The known side effects of the HPV vaccine include pain, redness or swelling at the injection site. In addition, because teens tend to faint more easily, fainting has been associated with vaccines given to this age group. Because of this, vaccine recipients should remain seated or lying down at the doctor’s office for about 15 minutes after getting the vaccine.
Reports of blood clots, strokes, heart attacks, chronic fatigue syndrome, infertility or premature ovarian failure, and even death have occurred after receipt of this vaccine; however, reviews of individual cases as well as controlled studies looking at groups of people who did and did not get the vaccine have shown that none of these problems were caused by the HPV vaccine.
My daughter is afraid to get the HPV vaccine because one of her friends said it hurts more than other vaccines. What can I tell her?
The HPV vaccine contains higher concentrations of salt than other vaccines, so they may hurt a bit more when they are administered. However, you can suggest one of the following to make your daughter more comfortable while getting the shot:
- Relax the muscle and look away while the shot is given. Take a few short, deep breaths and then a few longer breaths during the vaccine administration.
- Rub an alcohol pad on the opposite wrist right before the vaccine is given and then have her blow on it while the vaccine is administered.
- Use a distraction — friends, music, books, cell phones, or electronic games may work to distract your daughter during the vaccine administration.
- Finally, remind your daughter that the pain of the vaccine is minor compared to the pain associated with the disease.
What are the reactions to an HPV shot?
The HPV vaccine may cause redness, swelling and tenderness at the site of the injection. Some people may faint when they get the vaccine, so people are advised to stay at the doctor’s office for 15-20 minutes after getting the vaccine.
Friends and family often tell me the HPV vaccine is too new and it is difficult to find proper materials to answer this question. What do you tell parents who make this claim?
Because vaccines are given to healthy children, they are held to a strict standard of safety. What that means for us as consumers is that before a vaccine is ever recommended for the general population it has been tested in thousands and thousands of children through carefully controlled scientific studies. So while they are “new” recommendations, the vaccines have often been studied for years.
For example, HPV vaccines were tested in more than 30,000 women whose health was monitored for about seven years before the vaccine was approved and recommended. Long-term studies continued to monitor vaccine safety in about 190,000 women after the HPV vaccine was licensed. Similarly, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has networks that continue to monitor all vaccines in real time, so that any safety concern would come to attention quickly. At this point, millions of HPV vaccines have been given.
Why did my son have to wait 15 minutes after getting the HPV vaccine?
Some teens are more prone to fainting after getting the vaccine; therefore, all teens are recommended to wait at the doctor’s office for 15 minutes to be sure they are okay.
Questions about how HPV vaccine is made and works
Q. How long does it take for someone to be protected after getting the HPV vaccine?
A. It takes about two weeks after the first dose of vaccine for the immune system to generate an immune response. The additional doses make that response stronger, particularly the last one which fortifies the memory response.
Q. If I got the HPV vaccine, do I need to use protection?
A. It is important to understand that the HPV vaccine does not protect against other STDs, such as syphilis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, and herpes, nor does it protect against types of HPV to which one was already exposed. For these reasons, using protection is still prudent to consider.
I have had one dose of the HPV vaccine. Will I be protected if I become sexually active?
While you may have some protection after receiving the first dose of HPV vaccine, your best level of protection will occur after you receive all recommended doses.
I did not tell the doctor that I am sexually active before getting the HPV vaccine. Will it still work?
The HPV vaccine will not protect you against types of HPV to which you may have already been exposed; however, it will protect you against types to which you were not previously exposed. Since the vaccine protects against nine types of HPV, it is likely that you can still benefit from receiving the vaccine. For this reason, knowing your sexual activity status is not a requirement for deciding whether or not you should get the HPV vaccine.
How long does immunity last if you receive all doses of the HPV vaccine?
We do not know for sure whether immunity will last a lifetime; however, the data are reassuring. First, the vaccine has been studied for more than 10 years at this point, and immunity doesn’t appear to wane. Second, the immune responses generated by the vaccine are stronger than those invoked after natural infection. Finally, the hepatitis B vaccine, which is made using a technology similar to the HPV vaccine, induces a memory response that lasts at least 30 years.
If I got all necessary doses of the HPV vaccine, can I still develop genital warts?
Yes, it is possible. Although the HPV vaccine protects against the two strains of HPV that most commonly cause genital warts, it will still only prevent about 9 of every 10 cases of genital warts. Therefore, someone could still get genital warts if they are infected with a type of HPV that causes genital warts but was not in the vaccine.
I heard that the cervical cancer vaccine does not prevent all cases of cervical cancer. If this is true, aren’t people getting a false sense of security?
The strains of HPV included in the vaccine will prevent about 9 of 10 cases of cervical cancer. However, because a possibility of getting cervical cancer from one of the types of HPV not contained in the vaccine still exists, women should continue to get regular Pap tests. In addition, the vaccine does not protect against other sexually-transmitted diseases, so practicing safe sex is also important.
If my partner and I had the HPV vaccine, do we still need to use condoms?
Yes. The HPV vaccine does not prevent all types of HPV or other types of sexually-transmitted diseases. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has a helpful fact sheet about the use of condoms.
Will an HPV booster shot ever be required?
HPV booster doses are not expected to be necessary; however, public health officials will continue to monitor rates of disease to watch for waning immunity.
Can the HPV vaccine help me get rid of genital warts?
If you already have genital warts, the HPV vaccine will not treat them. However, the vaccine may still protect you against other types of HPV to which you were not previously exposed. Consult your doctor about medicines and procedures that may be used to treat genital warts.
Can the HPV vaccine cause HPV?
No. The HPV vaccine is made using a protein from the surface of the HPV virus. Although the protein folds itself to look like a viral particle in a microscope, it does not contain any genetic material, so it cannot replicate and cause an infection. Because the proteins look like a viral particle, scientists refer to them as “virus-like particles.”
Does the HPV vaccine protect me against any other sexually-transmitted diseases (STDs)?
No. The vaccine does not protect against any other STD. In fact, since there are more than 100 types of HPV, it does not even protect against all types of HPV.




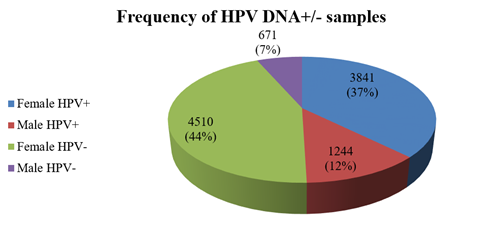

با سلام اگر یک خانم بر اثر این ویروس دچار سرطان دهانه رحم و سرطان رحم شود و بناچار این دو عضود برداشته شود . آیا بعد از برداشتن این اعضا معمولا ویروس هم از بدن وی پاک میشود یا همچنان ویروس در بدنش باقی خواهد ماند
بهتره بعد از عمل ایمنی بدن رو بالا نگه دارد تا در صورتی که ویروس در بدن باشد دفع شود. دوماه اول پک یک . سپس هفته ای ۴ روز مامشیسک تا ۶ماه . سپس دو روز تا دفع
سلام دکتر من اچ پی وی داشتم پر خطر شش سال درگیر بودم بعد این دو سال آخر از قارچ شما استفاده کردم اول پاپ اسمیرم خوب شد ولی اچ پی وی هنو مثبت بود الان آزمایش دادم اچ پی وی ام منفی شد دکتر دست به خاک میزنی طلا بشه انسان های مثل شما تو دنیا کم هستن خدا همیشه پشت پناهت باشه همیشه دعات میکنم که قارچها باعث شد من از این همه استرس این بیماری خلاص شم.دکتر هر چی از خدا میخایی بهت بده من خیلی امروز خوشحالم.
الحمد اله. تبریک. مرسی که اطلاع دادید.
سلام دکتر
۳۳ سالمه و تقریبا ۷ یا ۸ ماهی میشه انتهای گلوم زیر لوزه هام دونه های قرمز رنگ داره که موقع قورت دادن آب دهن احساس میکنم چیزی تو گلوم هست و دو هفته ای میشه که دون دون های قرمز به زیر زبونم سرایت کرده و درد داره لطفاً راهنمایی کنید
ایمنی بدنتو بالا ببر. اکثر بیماری های عفونی ویروسی باکتریایی مهار میشه. با پزشک هم مشورت کن و علتشو در بیار که بهتر بشه برنامه بت داد. اگه برات امکان پذیر نیست مصرف یک گرم ماشمیکس رو شروع کن برای دوماه. کمتر شد ادامه بده
سلام خسته نباشید من 18سالمه و 5یا 6ساله پیش رابطه داشتم بعد اون رابطه کمی پایین تر از کلاهک التم دونه های زیادی زد که فک کنم جوش بود بعد از 1ماه از بین رفت و الان که نگاه میکنم ی دونه های سفتی اونجا وجود داره خواستم بگم میتونه زگیل باشه درضمن هیچ گونه درد و خارش و سوزشی نداره و نمیدونم کی به وجود اومدن احتمالاا بعد از جوش ها لطفا کمکم کنید
ممکنه الرزی باشه. اگه بیش از یکماه طول کشید و از بین نرفت با آزمایش مشخص میشه که زگیل هست یا نه.
اگه تعدادشون ثابت موند با سبک زندگی سالم اون رو دفع کنید. اگه تغییر کرد با ما ارتباط بگیرید و مصرف قارچ رو شروع کنید.
سلام دکتر تست hpv۸ماه پیش من منفی بودبدلیل عفونت شدیددکترجدیدمن بازبرام hpvنوسی اینبارhpvپرخطر تیپ۳۵تشخیص داده شد برام سواله چطورممکنه درسن۲۲سالگی ودرعرض۸ماه ب این ویروس مبتلا شده باشم ازشریک جنسیمم چ قبل ازدواج چ الان مطمئنم اهل یک سری ازروابط نیست پس این لعنتی ازکجااومده
راه های انتقال ویروس زیاده. ممکنه از راههای دیگه به شما منتقل شده باشه.
سلام دکتر دیروز جواب آزمایش یکی از بستگان اومده که high risk:58_51_82 و Low risk _40_6 بود الان یعنی خیلی خطرناکه ؟ امکان سرطان هست؟ میشه درمانش کرد؟ ممنون میشم کامل جواب بدین 🙏
همانطور که قبلا گفته شد تعداد و نوع ویروس برای روش درمانی ما مهم نیست. همه رو میشه منفی کرد. با توجه به داشتن یا نداشتن عفونت برنامه رو بگیره و شروع کنه.